Note: Adjusting file permissions is only recommended for advanced users. In most cases, changing file permissions is not necessary, and it’s best to keep the default values.
On web hosting packages, you can change file permissions through the control panel using the File Manager. In many SFTP programs, you can set the permissions of a folder by going to the properties or by right-clicking on the file or folder in question. Via SSH, you do this with the CHMOD command.
In this article, we will first explain how file permissions work, and then how you can change them.
How do file permissions work?
The structure is always divided into three parts:
- First, the User – The user who created the file.
- Then, the Group – A group of users with shared access.
- And finally, Others (sometimes called World) – Everyone who is not the User or the Group.
This order is always used when changing or expressing permissions. File permissions can be represented in two ways: using symbols (letters) or numbers.
For symbols:
- r = read
- w = write
- x = execute
- - = no permission
When the User has all permissions, but the Group and Others only have read and execute permissions, it looks like: drwxr-xr-x, where the d means it’s a directory (folder). If it’s a file, it’s shown with a - (-rwxr-xr-x).
In numbers:
- 4 = read
- 2 = write
- 1 = execute
- 0 = no permission
When you add these numbers together, you can specify permissions for each group (user/group/others) more compactly. For example, 755 means the User has all (4+2+1=7) permissions, while the Group and Others only have read and execute (4+1=5).
Changing file permissions in the File Manager
Within your control panel, go to 'Web Hosting' via the left-hand menu. Then click on your domain name under 'Products'.
Now click on 'File Manager' on the right-hand side of the overview.
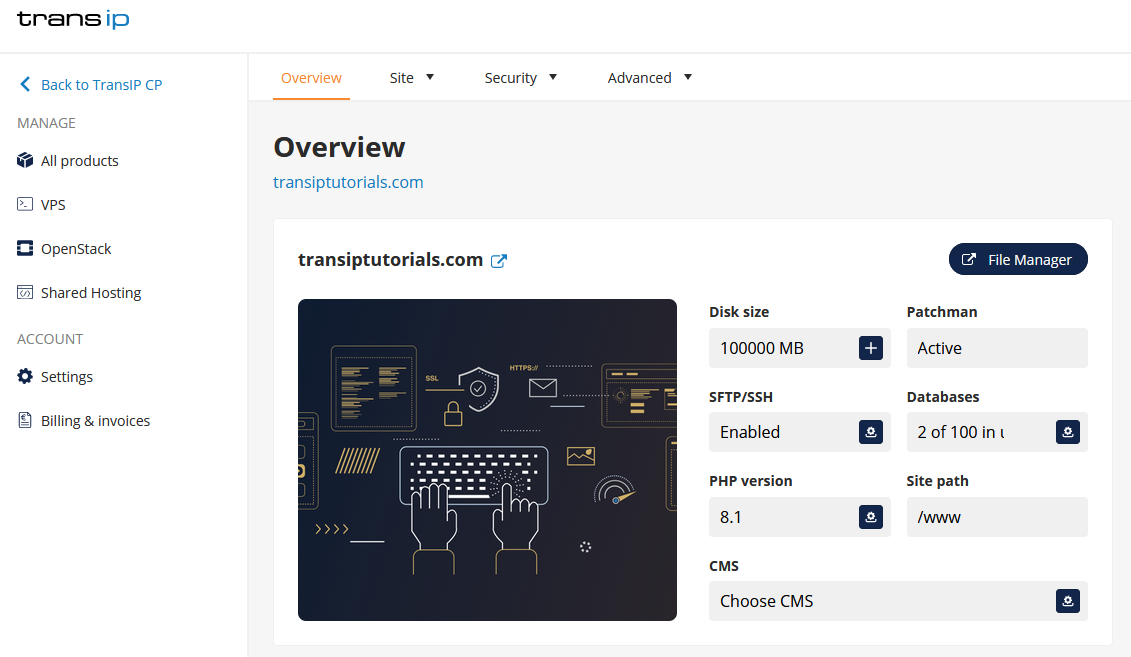
You’ll now see an overview of the website folders located in your web hosting package. At the top right, you’ll find the 'Permissions' column, where you can view the current permissions for each folder or file.

When you click on the permission structure, a menu opens where you can change the permissions.

You can change the file permissions in two ways: by checking or unchecking the appropriate boxes (read/write/execute), or by entering the permission numbers under 'Manual'.
Changing write permissions in SFTP
When connected with an SFTP program, you can usually right-click on the file or folder whose permissions you want to modify. Then click on ‘File Attributes’ to make changes.

Changing write permissions in SSH
When connected via SSH, you can change file permissions using the chmod command.
chmod 755 example.txtYou can check the permissions with the following command:
ls -l filename



